Warehouse automation is transforming the automotive sector by improving speed, accuracy, and cost efficiency across the supply chain. Many automotive manufacturers have already embraced automated systems to optimize their warehouse operations, streamline inventory management, and meet growing demand. Here are several real-world examples of how warehouse automation is benefitting automotive companies.
1. BMW’s Automated Parts Warehouse


Location: Leipzig, Germany
Automation Technology: Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs), Robotic Systems, and ASRS
BMW is a prime example of how automation can streamline automotive production. At its Leipzig plant, the company has integrated an advanced Automated Storage and Retrieval System (ASRS) to handle the vast inventory of parts that go into assembling various car models. The system helps store and retrieve parts with high speed and precision, ensuring that the right components are delivered just in time to the production line.
BMW also uses Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) to transport components across the warehouse, reducing the need for human labor in the transportation of heavy or bulky items. AGVs are programmed to follow predetermined paths or can be dynamically routed through the facility based on real-time needs.
The result? BMW has reduced errors in parts delivery, improved efficiency, and lowered inventory costs, all of which contribute to more streamlined and cost-effective production.
2. Daimler’s Mercedes-Benz Automated Logistics Center
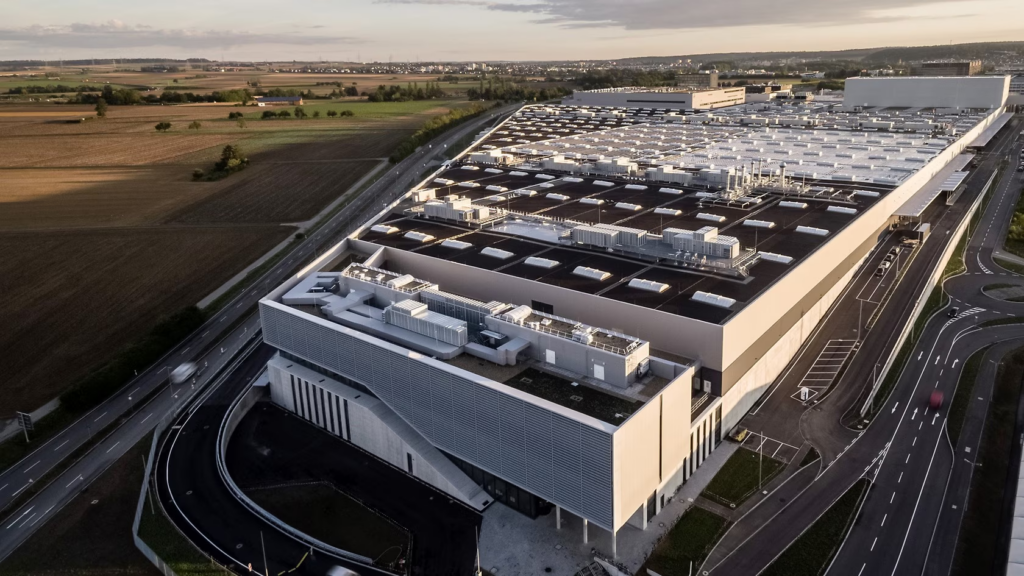


Location: Stuttgart, Germany
Automation Technology: Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs), Robotic Pickers, and Warehouse Management Software (WMS)
Daimler has also embraced automation at its Mercedes-Benz logistics center in Stuttgart, Germany. The facility is equipped with a fleet of AGVs that transport parts between different sections of the warehouse. These robots work autonomously to move items such as engines, transmission systems, and other vehicle components from one area to another with minimal human intervention.
In addition, robotic pickers are used to automatically retrieve and place parts onto assembly lines based on real-time orders, ensuring high levels of accuracy. By integrating automated guided vehicles with its Warehouse Management Software (WMS), Daimler has created a system where inventory levels are constantly monitored, and the most needed parts are delivered in the correct sequence without any delays.
The impact has been impressive: Mercedes-Benz’s facility can now ship thousands of parts per day with minimal errors and greater flexibility in production scheduling. The automated system reduces human error, improves safety, and boosts productivity by speeding up the entire process.
3. Ford’s Use of Robotics in Its Michigan Warehouse

Location: Michigan, USA
Automation Technology: Collaborative Robots (Cobots), Robotic Arms, and Automated Storage Systems
At Ford’s Michigan warehouse, automation is playing a key role in reducing costs and improving efficiency. One of the key technologies employed is collaborative robots (cobots). These cobots work alongside human workers to assist in tasks like picking and packing small automotive parts. These robots are designed to be flexible and easy to reprogram, which means they can adapt to the constantly changing demands of the automotive manufacturing process.
Ford also uses robotic arms for heavy lifting and moving automotive parts, including larger items like engines, chassis, and wheels. These robotic systems are equipped with sensors that allow them to handle parts delicately while reducing the risk of damage during transport.
By automating both the heavy lifting and smaller, repetitive tasks in its warehouse, Ford has been able to reduce labor costs and improve its production efficiency. Additionally, workers are freed up to focus on higher-value tasks like quality control and system maintenance.
4. Volkswagen’s Intelligent Warehouse in Mexico
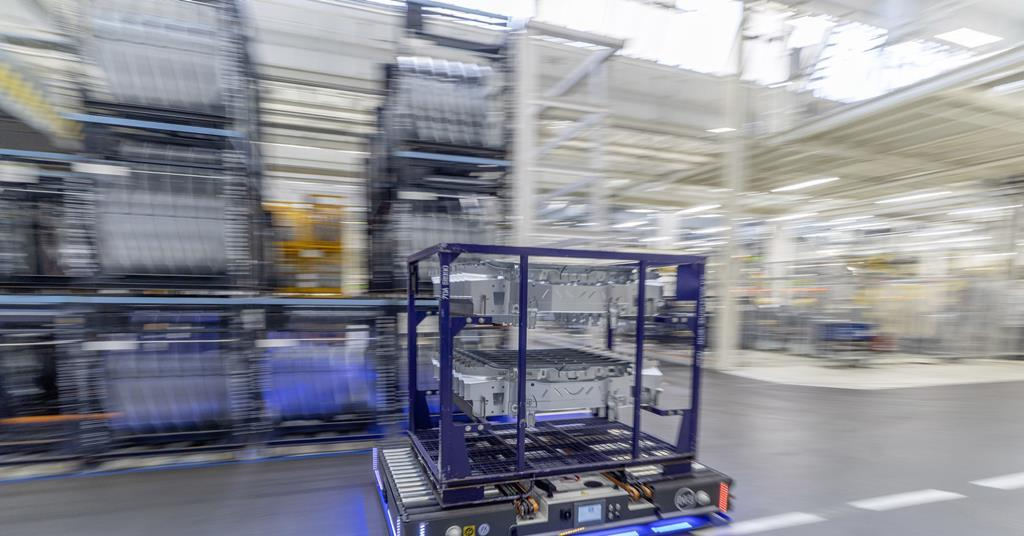


Location: Puebla, Mexico
Automation Technology: Robotic Sorting Systems, AGVs, and RFID Technology
Volkswagen’s Puebla plant in Mexico is one of the company’s most advanced facilities when it comes to warehouse automation. The plant uses robotic sorting systems to manage the delivery and sorting of auto parts, including tires, engines, and suspension components. This system allows Volkswagen to rapidly move parts through the warehouse without human intervention, reducing errors and increasing processing speed.
At the heart of Volkswagen’s operations is its use of Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) technology. RFID tags are attached to all parts entering the warehouse, and the system continuously tracks their movement throughout the facility. This real-time tracking allows for precise inventory management and helps the company avoid stockouts or overstocking. With these automated technologies in place, Volkswagen is able to maintain a just-in-time inventory system, ensuring that parts are delivered to assembly lines without delays.
Volkswagen’s warehouse automation has had a measurable impact on operational efficiency. The plant has significantly reduced inventory holding costs and improved order fulfillment speed, allowing it to stay competitive in the fast-paced automotive market.
5. Toyota’s High-Tech Parts Distribution Center in the U.S.
Location: Kentucky, USA
Automation Technology: Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs), Robotic Arms, and Machine Learning Algorithms
At Toyota’s parts distribution center in Kentucky, automation has enabled the company to optimize its logistics and improve its supply chain resilience. The facility uses Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) to transport parts and materials across the warehouse, reducing the need for manual labor and speeding up operations. These vehicles are equipped with sensors and navigation technology that allow them to avoid obstacles and adapt to changing workflows in real-time.
Moreover, Toyota has integrated robotic arms and machine learning algorithms into its system to further enhance efficiency. The robotic arms automatically sort, pack, and label parts, while machine learning algorithms analyze patterns in parts orders to predict future demand. This helps Toyota optimize warehouse space and anticipate inventory needs, allowing the company to meet the fluctuating demands of its assembly lines with greater accuracy.
This investment in automation has resulted in faster turnaround times for parts delivery and a more agile supply chain, helping Toyota remain efficient and responsive to customer needs.
6. Nissan’s Use of Automated Inventory Systems in its UK Warehouse
Location: Sunderland, UK
Automation Technology: Automated Storage and Retrieval Systems (ASRS), RFID, and Automated Sorting
At Nissan’s Sunderland plant in the UK, automation is integrated into every aspect of the parts warehouse. The facility employs Automated Storage and Retrieval Systems (ASRS) to efficiently manage the high volume of parts that flow in and out of the warehouse each day. ASRS systems are designed to store items at optimal heights and retrieve them quickly, allowing Nissan to maximize storage capacity and reduce time spent searching for parts.
RFID technology enables real-time tracking of all components, providing visibility throughout the entire warehouse. This has helped Nissan improve inventory accuracy, eliminate discrepancies, and reduce the risk of delays due to missing parts.
Additionally, automated sorting systems ensure that parts are packaged and delivered to the correct location in the correct quantity. This reduces the manual handling of parts, speeds up the distribution process, and ensures that parts are always available when needed.
Link to a complete walk through of the NISSAN UK plant – https://www.cnet.com/pictures/nissan-uk-plant-robots-humans-pictures
7. Tata Motors’ Warehouse Automation at Pune Plant
Location: Pune, India
Automation Technology: Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs), Robotic Arms, and Real-Time Inventory Management Systems
Tata Motors, one of India’s largest automotive manufacturers, has also embraced warehouse automation to streamline operations at its Pune plant. As part of its effort to enhance efficiency and reduce human error, Tata Motors has integrated Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) into its warehouse system. These AGVs are responsible for transporting automotive parts, including engine components and assembly kits, across the facility. With minimal human intervention, the AGVs ensure fast and efficient movement of materials from storage to the assembly line.
In addition to AGVs, the Pune plant uses robotic arms to handle heavier or repetitive tasks, such as picking and sorting parts. These robots perform with precision, improving both the speed and accuracy of these processes. By automating these tasks, Tata Motors has been able to minimize the potential for errors caused by human fatigue or inconsistencies.
Tata Motors has also implemented a real-time inventory management system at the Pune plant. Using technologies like RFID, the plant tracks the movement and quantity of components, helping to maintain accurate inventory levels and improve the decision-making process for restocking and part replenishment. This ensures that the correct parts are always available for the production line, preventing downtime and delays in manufacturing.
The results of this investment in warehouse automation at Tata Motors’ Pune plant include a significant reduction in labor costs, improved safety, and enhanced operational efficiency. Moreover, the increased accuracy of inventory management has helped to reduce excess stock and minimize waste, contributing to a more sustainable and cost-effective production process.
Conclusion: The Road Ahead for Warehouse Automation in the Automotive Industry
The real-life examples from BMW, Daimler, Ford, Volkswagen, Toyota, Nissan and Tata highlight the transformative effects of warehouse automation in the automotive industry. These companies are leveraging a combination of robotic systems, AGVs, RFID technology, and AI-powered warehouse management solutions to optimize their operations, reduce costs, and increase efficiency.
As automotive manufacturing continues to evolve, warehouse automation will only grow in importance. The ability to move parts quickly, manage inventory accurately, and meet demand without delays is a key driver for success in the competitive automotive industry. With advances in technology, the future of automotive warehouse operations looks even more efficient, scalable, and responsive to market demands.


